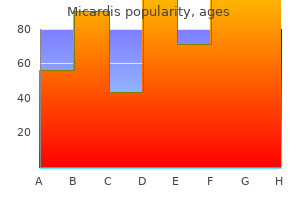
"Micardis 80 mg low price, heart attack telugu movie".
By: Y. Redge, M.B.A., M.D.
Professor, Medical College of Wisconsin
The disadvantages of this product are similar to blood pressure chart dr oz purchase micardis 40mg visa those of branched-chain solutions: its expense and the lack of prospective heart attack 40 year old male cheap micardis 40 mg online, randomized trials confirming its efficacy pulse pressure transducer order micardis uk. Parenteral nutrition supplementation with the amino acid glutamine is undergoing investigation. Currently, glutamine is not present in commercially available parenteral nutrition solutions in the United States because it has a shorter shelf life than the more commonly used amino acids and has been considered a non-essential amino acid. During critical illness, however, glutamine appears to be an essential amino acid for the intestinal tract. For patients undergoing bone marrow transplantation, the use of glutamine-supplemented parenteral nutrition (as compared with the standard amino acid solution) has been shown to improve clinical outcome with fewer infections and shortened hospital stay. Parenteral carbohydrate provided in the form of dextrose is a vital source of fuel and has important nitrogen-sparing effects. Solutions of dextrose in concentrations of 10 to 70% are mixed with the appropriate quantity of amino acids to obtain the desired solution. The minimum daily glucose requirement is the amount necessary to meet brain glucose needs (100 to 150 g) because body carbohydrate stores are limited. Providing calories as glucose stimulates insulin secretion, reduces muscle protein breakdown, and decreases hepatic glucose release, thus decreasing the need for skeletal muscle to provide amino acid precursors for gluconeogenesis. Fat emulsions provide an intravenous source of fat calories and the essential linoleic and linolenic fatty acids. The emulsions contain long-chain fatty acids (derived from safflower and/or soybean oil), egg yolk phospholipids as emulsifying agents, and glycerin to make the solution isotonic with plasma. Intravenous fat is calorically dense (9 kcal/g), isotonic, and protein sparing and can prevent essential fatty acid deficiency. In addition, provision of a portion of calories as fat allows lower rates of dextrose infusion, which results in less hyperglycemia and hyperinsulinemia and a lower incidence of abnormalities in liver function tests. The fat can be administered intravenously either by piggyback infusion or as a three-in-one admixture of fat, dextrose, and protein in one container. The fat emulsion is hydrolyzed by lipoprotein lipase to free fatty acids and glycerol. When fatty acids are oxidized for fuel, the respiratory quotient and therefore carbon dioxide production rates are lower than those observed if carbohydrate or protein is oxidized; this feature may be advantageous in certain clinical situations such as severe pulmonary disease. Adverse effects, including hypoxemia, hepatic dysfunction, and impaired immune function from fat uptake by the reticuloendothelial system, have been reported with intravenous fat administration. At very high infusion rates, enzymatic removal systems for free fatty acids become saturated and hypertriglyceridemia can result. However, all of these effects have been demonstrated at the higher infusion rates achieved during 8- to 12-hour infusions rather than during 24-hour infusions. No data suggest that the continuous infusion of intravenous fat emulsion at recommended rates to normolipidemic patients results in any adverse effects. If the plasma triglyceride concentration exceeds 400 mg/dL, the intravenous fat emulsion infusion rate should be reduced or the infusion discontinued. Although the optimal percentage of calories that should be infused as fat is unclear, provision of 20 to 30% of total calories as fat is generally recommended for stressed patients receiving parenteral nutrition. The electrolytes and minerals required for health are sodium, potassium, chloride, calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, and sulfur. Most sodium and potassium cations are added to the parenteral nutrition solution as chloride or acetate salts after the phosphate requirement is met. Acetate is further metabolized by the liver to bicarbonate to provide an alkaline buffer. Trace elements are commercially available as combination products or as single-item injections; 1 mL of a multiple trace element injection contains zinc, copper, manganese, and chromium in amounts that are suggested for medically stable adult patients (Table 230-1). Because iron, iodine, and selenium are not always added to parenteral nutrition solutions, monitoring of levels and supplementation of these trace elements may be required for patients receiving longer-term administration of parenteral nutrition. The composition of intravenous multivitamin products has been established in accordance with the guidelines of the American Medical Association Nutrition Advisory Group. One adult multivitamin formulation and one pediatric multivitamin formulation are currently available commercially. The adult formulation provides the daily maintenance for three fat-soluble and nine water-soluble vitamins (Table 230-2).
The organisms live for approximately 1 month on the scalp but are able to arrhythmia medication buy micardis 20 mg line live only a few days (as long as a week) if removed from the warmth and blood meals available on the scalp heart attack 10 year risk calculator purchase micardis 20mg mastercard. Infestation of scalp hairs produces severe itching and occasionally secondary pyogenic infection and cervical lymphadenopathy pulse pressure 40 purchase micardis 80mg with amex. Lice may be visible crawling on hair shafts and they may move quite rapidly, approximately 23 cm/minute. The patient should shampoo, rinse, and dry the hair; then apply it to the hair and scalp. As a result of growing resistance, there may be treatment failure with 1% permethrin, in which case 5% permethrin (Elimite) or a single oral dose of ivermectin (200 mug/kg) can be tried. When the patient is treated, all infested family members should be treated simultaneously. Combing the nits reduces the number of viable ova and decreases the chance of relapse and treatment failure. Body lice are seen in cold climates (because of heavy clothing) and under conditions of crowding and poor sanitation. Lice and eggs are found in the seams of clothing, and very few lice are seen on the body of patients. The lice favor clothing fibers, especially wool, and live in the clothing, visiting the body only to feed. Ultimately, excoriations, urticaria, pigmentary changes, and secondary infection may occur. Body lice are also a vector for serious diseases of humanity, including typhus (Rickettsia prowazekii), trench fever (Bartonella quintana), and relapsing fever (Borrelia recurrentis). Treatment of body lice requires only improved hygiene and cleaned clothing in mild cases. Crab lice are transmitted predominantly by sexual contact, clothes, or infected hairs. Although typically found on pubic hair, crab lice occasionally infect other short hairs of the body, including eyebrows, eyelashes, the edge of the scalp, moustache, and axilla. On close inspection, nits are visible, and the louse may be seen clinging to one or two hairs. Also evident in these infestations are dried serous fluid, blood, and louse feces. The combination of louse saliva and blood produces a blue-gray macule known as macula caerulea. It is also important to clean bedding and clothing, which should be washed in hot water. Treatment failure often results from not treating other involved areas of the body. Infestation of the eyelid can be treated with petrolatum occlusions, yellow oxide of mercury ointment, or mechanical removal of nits. Sexual partners and intimate contacts should be treated when they have evidence of lice. Children with pubic lice infestation in facial hair or eyes should be evaluated for the possibility of sexual abuse. Symptomatic treatment of pruritus in all types of lice infestation consists of antihistamines, and, in some cases, topical corticosteroids may be applied to affected areas for additional symptomatic relief. The most common beetle injury is not from a bite or sting but from the formation of blisters. This beetle fills its breathing tube with air and closes its breathing pores to elevate body pressure. Clues to this cause of blisters are the presence of multiple blisters in the same stage of development and the lack of an accompanying rash. Sometimes the blisters form a line, reflecting the path of the beetle as it crossed the skin. Cantharidin has been prepared commercially and used as a diuretic, aphrodisiac, and rubefacient.
Region A near the N terminus is highly variable 2014 generic micardis 80mg without a prescription, and antibodies to hypertension recipes cheap micardis 80 mg overnight delivery this region confer type-specific protection causes 0f hypertension purchase micardis 80 mg without a prescription. Within the more conserved B to D regions lies an area that binds one of the complement regulatory proteins (factor H), stearically inhibiting antibody binding and complement-derived opsonin deposition and effectively camouflaging the organism against humoral immune surveillance. Observations by Lancefield suggest that the quantity of M protein produced decreases with passage on artificial media and conversely increases rapidly with passage through mice. The quantity of M protein produced by an infecting strain progressively decreases during convalescence and during prolonged carriage. Cholesterol inhibits toxicity 1621 in isolated myocytes and hemolysis of red blood cells in vitro. Streptolysin S is a cell-associated hemolysin that does not diffuse into the agar media. Purification and characterization of this protein have been difficult, and its only role in pathogenesis may be in direct or contact cytotoxicity. Dnases may also contribute to cytokine production, although their importance in pathogenesis has not been established. This extracellular enzyme hydrolyzes hyaluronic acid in deeper tissues, thereby facilitating the spread of infection along fascial planes. The gene for pyrogenic exotoxin A (speA) is transmitted by bacteriophages, and stable production depends on lysogenic conversion in a manner analogous to diphtheria toxin production by Corynebacterium diphtheriae. Patients with streptococcal pharyngitis have an abrupt onset of sore throat, submandibular adenopathy, fever, and chilliness but not usually frank rigors. The uvula is edematous, tonsils are hypertrophied, and the pharynx is erythematous with exudate that may be punctate or confluent. Depending on the infecting strain, pharyngitis may progress to scarlet fever, bacteremia, suppurative head and neck infections, rheumatic fever, post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis, or streptococcal toxic shock syndrome. Pharyngitis is usually self-limited, and pain, swelling, and fever resolve spontaneously in 3 to 4 days even without treatment. Definitive diagnosis is difficult when based only on clinical parameters, especially in infants, in whom rhinorrhea may be the dominant manifestation. Even in older children with all the preceding physical findings, the correct clinical diagnosis is made in only 75% of patients. Rapid antigen detection tests in the office setting have a sensitivity and specificity of 40 to 90%. A popular approach in clinical practice is to obtain two throat swab samples from the posterior of the pharynx or tonsillar surface. A rapid strep test is performed on the 1st, and if it is positive, the patient is treated with antibiotics and the 2nd swab discarded. If the rapid strep test is negative, the 2nd sample is sent for culture, and treatment is withheld pending a positive culture. During the last 30 to 40 years, outbreaks of scarlet fever in the western world have been notably mild, and the illness has been referred to as "pharyngitis with a rash" or "benign scarlet fever. The fatal or malignant forms of scarlet fever have been described as either septic or toxic. These cases occurred before the advent of antibiotics, antipyretics, and anticonvulsants, and sudden deaths were the result of uncontrolled seizures and hyperpyrexia. In contrast, children with septic scarlet fever had prolonged courses and succumbed 2 to 3 weeks after the onset of pharyngitis. Complications of streptococcal pharyngitis and malignant forms of scarlet fever have been less common in the antibiotic era. Even before antibiotics became available, necrotizing fasciitis and myositis were not described in association with scarlet fever. Distinctive features are well-defined margins, particularly along the nasolabial fold, scarlet or salmon-red rash, rapid progression, and intense pain. Flaccid bullae may develop during the 2nd to 3rd day, yet extension to deeper soft tissues is rare.
Purchase micardis 80 mg visa. Review of the WiFi Bathroom Scales (Withings ws-50 vs Fitbit aria).
The erythrocyte sedimentation rate is increased acutely but normalizes over several weeks hypertension categories order micardis 80mg fast delivery, even with continued joint symptoms arterial insufficiency generic micardis 80mg online. Synovial fluid changes are not striking: cell counts of 1000 to blood pressure zetia cheap micardis online visa 60,000, predominantly mononuclear, normal viscosity. In Australia patients seldom have viremia on presentation, whereas in the Pacific outbreak viremia was readily detected. Sindbis virus has caused disease in Egypt, elsewhere in Africa, in Europe, and in Australia. Human infection is common where birds and Culex mosquitoes are in close proximity. Because Sindbis and West Nile fever virus share the same transmission cycles, Sindbis transmission often parallels that of West Nile fever virus. In northern Europe, symptomatic disease appears in late summer between 60 and 65 degrees of north latitude, usually affecting adults with forest occupations. Clinically, fever is low grade and is accompanied by malaise, myalgia, rash, and arthralgia in wrists, ankles, knees, and elbows. The rash begins on the trunk as scattered macules and spreads to the extremities, palms, and soles. Unlike that caused by other alphaviruses, the rash frequently becomes vesicular, especially on the feet and hands. In Sweden, more than 20% of patients had joint symptoms longer than 1 month after onset. Hantaviruses are maintained by a single rodent reservoir species belonging to the subfamily sigmodontinae (Peromyseus maniculatus [deer mouse], P. Humans are infected by exposure to aerosols of secretions and excretions from infected rodents. The major abnormality is thought to be an increase in vascular permeability via an immunopathologic mechanism. The disease begins abruptly with fever and myalgia, often accompanied by gastrointestinal symptoms and headache; it is indistinguishable from other nonspecific acute febrile illnesses such as influenza. The patient first notes cough and dyspnea, but acute pulmonary edema and hypotension develop rapidly in most patients. Polymerase chain reaction and immunohistochemical staining can detect virus in tissue. The disease is of particular concern in the Americas not only because of its multiple etiologic agents and widespread occurrence but also because of its concurrent affliction of domestic animals and humans and its potential for epidemic spread. The most important arthropod-borne viruses that cause encephalitis are shown in Table 392-2. The ratio of inapparent to clinically overt infections is a distinctive, age-dependent quality of each disease. The neurologic disease usually begins after a variable period of nonspecific, systemic symptoms and may take the form of aseptic meningitis, meningoencephalitis, or encephalitis. These syndromes are not distinguishable on clinical grounds alone from similar syndromes caused by other infectious agents. Two pathologic processes are common to the arboviral encephalitides: (1) neuronal and glial damage mediated by intracellular viral infection and (2) migration of immunologically active cells into the perivascular space and brain parenchyma. Endothelial cell swelling and proliferation, destruction of myelin sheaths in deep white matter areas, and vasculitis are present in some arboviral encephalitides. After a bite by an infected arthropod, viral replication occurs in local tissues and in regional lymph nodes. Viremia, which seeds extraneural tissues, occurs and persists depending on the extent of replication in extraneural sites, the rate of viral clearance by the reticuloendothelial system, and the appearance of humoral antibodies. Many alphavirus and flaviviruses involve striated muscle and vascular endothelium, whereas Venezuelan encephalitis virus is associated with myeloid and lymphoid tissue invasion. During this viremia, the neural parenchyma may be invaded, but the mode of penetration of virus across the blood-brain barrier is not completely understood. Possible mechanisms include passive movement of virus across vascular membranes and virus replication in cerebral capillary endothelial cells. The immature brain is more susceptible to damage by western equine, Venezuelan equine, and California encephalitis viruses (see Table 392-3). Louis encephalitis principally affects the elderly, whereas Japanese encephalitis and eastern equine encephalitis have a bimodal incidence, striking both children and elderly persons. In endemic areas, immunity accumulated with increasing age may reduce the incidence of disease in older persons for some viruses; however, the reasons for increased severity of illness with other viruses remain unknown.