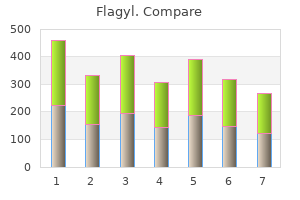
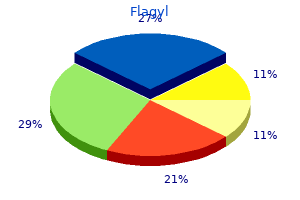
"Order flagyl 500 mg fast delivery, effective antibiotics for sinus infection".
By: X. Kamak, M.A., M.D., M.P.H.
Deputy Director, Harvard Medical School
Two studies conflicted when evaluating whether the presence of paraneoplastic antibodies have prognostic implications40 antibiotics for acne tetralysal buy generic flagyl 500 mg online,41; the utilization of different techniques to virus wot order genuine flagyl line measure antibody levels may account for the discrepant results infection control and hospital epidemiology flagyl 500 mg visa. Various therapies such as plasma exchange and immunosuppressive therapy with agents such as corticosteroids, cyclophosphamide, and tacrolimus have been tried, but generally offer little benefit. In patients with Lambert-Eaton syndrome, two randomized placebo-controlled trials of 3,4 diaminopyridine, which blocks potassium channel efflux from nerve terminals, demonstrated that treatment with this agent increases compound muscle action potentials and significantly improves muscle strength. Patients with a malignant effusion are appropriate to exclude from a combined modality treatment because hemithoracic radiotherapy to encompass the entirety of the pleura is impractical. The presence of supraclavicular lymphadenopathy commonly is associated with extensive disease but, when encountered in patients with otherwise limited disease (5% of cases), carries a trend toward poorer survival. However, two studies that evaluated twice-a-day radiation regimens excluded patients with contralateral hilar disease to reduce the normal lung volume irradiated and the risk for toxicity. If there is evidence of a pleural effusion, a thoracentesis or thoracoscopy may help confirm that the effusion is nonbloody, transudative, and cytologically negative. Effusions too small to permit image-guided sampling should not be considered in staging. More favorable outcomes of patients have been reported in patients previously classified as very limited disease. If a patient is a current smoker, he or she should be advised to quit immediately in the strongest terms and offered the most aggressive smoking cessation intervention available. Patients with limited-stage disease should receive the chemotherapy concurrently with twice-daily thoracic irradiation beginning with the first, second, or third cycle. Because the toxicity of all treatment worsens and effectiveness lessens in patients with a low performance status, clinicians must carefully evaluate the agent(s) used and the appropriateness and goals of therapy individually. For many patients in this low performance status group, supportive care only and referral to hospice are the best options. Clinical and Serologic Predictive and Prognostic factors Multivariable analyses suggest that performance status is a strong and reproducible predictive and prognostic factor. Older age has been associated with decreased performance status and more comorbid illnesses and often results in compromised chemotherapy dose intensity,63,64 which may partially explain its prognostic implications. Certain metastatic sites, such as the liver,6567 the brain,66,68 bone marrow,67 and bone,68 as well as the total number of metastatic sites involved,47 have been found to be of prognostic significance for patients with extensive-stage disease. Paraneoplastic Cushing syndrome has been correlated with a poor response to therapy and short survival. Alkylating agents, anthracyclines, vinca alkaloids, and antifolates all showed single-agent efficacy. In the 1980s, the epipodophyllotoxin, etoposide, and the platinum analogs, cisplatin and carboplatin, were introduced, and their activity ranged from 40% to 60% in previously untreated patients. Ultimately, randomized trials of combinations demonstrated superior activity to single agents. For patients with extensive disease, the complete response rate was 14%, the overall response rate was 57%, and the median survival was 26 weeks. For patients with limited disease, the rates were 41%, 75%, and 52 weeks, respectively. In addition, both agents could be given at full doses because of less myelosuppression with cisplatin. Randomized trials comparing cisplatin and carboplatin suggest that they may have similar efficacy. The Hellenic Cooperative Oncology Group randomized 147 patients with either limited or extensive disease to receive etoposide 100 mg/m2 days 1 to 3, and cisplatin 100 mg/m2 or carboplatin 300 mg/m2. Nausea, vomiting, nephrotoxicity, and neurotoxicity were significantly lower in the patients who received carboplatin, as was grade 4 leukopenia. However, the sample size of this study is inadequate to confirm equivalent efficacy. Although hematologic toxicities were higher in those patients that receive carboplatin, nonhematologic toxicities were increased in those that receive cisplatin. More recently, platinum combinations with topotecan and irinotecan have emerged as potential regimens for initial therapy.
Vector-borne transmission of nosocomial infectious disease is rare in developed countries antibiotic diarrhea discount flagyl uk. Strategies for Preventing Transmission of Nosocomial Pathogens In 1994 the Hospital Infection Control Practices Advisory Committee of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention issued general guidelines designed to bacteria 4 result in fecalysis purchase generic flagyl pills prevent the transmission of infectious agents within hospitals antibiotics for dogs and humans buy cheap flagyl online. The first tier, termed "standard precautions," is designed to prevent the transmission of microorganisms from moist body substances, including blood. Standard precautions are designed to be used by health care workers during all patient contacts, even when 1582 the patient is not known to be infected or colonized with an important nosocomial pathogen. To prevent percutaneous injury, standard precautions also call for preventive measures in handling needles, scalpels, or other sharp devices. An additional tier of control measures termed "transmission-based precautions" may be used (in addition to standard precautions) during care of patients known to be infected or colonized with an infectious agent that can be transmitted via contact, airborne, or droplet transmission. For example, when a patient is infected or colonized with epidemiologically important microorganisms transmitted primarily by contact. Airborne precautions involve the use of protective respiratory masks by health care workers and private patient rooms equipped with negative-pressure ventilation systems that discharge air either to the outdoors or through high-efficiency air filtration systems. The non-fermentative gram-negatives Pseudomonas aeruginosa (and other Pseudomonas spp. Gram-positive bacteria have become increasingly prominent nosocomial pathogens in recent years. Other bacterial nosocomial pathogens of note include Legionella pneumophila, an important cause of nosocomial pneumonia, and C. The high prevalence of methicillin resistance among the two most common gram-positive nosocomial pathogens, S. In the last two decades, fungi have played an increasingly important role in nosocomial infections. Their emergence is related to several factors, including advances in cancer therapy and organ transplantation, which have led to highly immunocompromised inpatient populations, and the widespread use of broad-spectrum antibiotics, which provide a selective advantage for opportunistic fungi. Candida species are now the fourth most common cause of nosocomial bloodstream and urinary tract infections in the United States, and they account for almost 75% of all nosocomial fungal infections. Candida albicans Klebsiella pneumoniae Gram-positive anaerobes Proteus mirabilis Other Streptococcus spp. Other Enterobacteriaceae-aerobes Other gram-positive aerobes Viruses Bacteroides fragilis *Pathogens with fewer than 1% of the isolates at all sites are not shown. These fungi are transmitted by inhalation of airborne fungal conidia and usually cause necrotizing bronchopneumonia, sinusitis, or rhinocerebral disease. Hospital reservoirs of Aspergillus include unfiltered air, ventilation systems, and contaminated dust generated during hospital construction. Other emerging fungal pathogens include the yeast Malassezia furfur (a cause of fungemia often associated with infusion of intravenous lipids because it requires exogenous lipid for growth), Trichosporon spp. Influenza is an important cause of morbidity and mortality in health care institutions, not only acute care hospitals but also long-term care facilities such as nursing homes. Control measures include new case surveillance, droplet (some prefer airborne) precautions for known or suspected cases, vaccination of health care workers, and in outbreak situations, prophylactic antiviral therapy with rimantadine or amantadine. Susceptible health care workers are an important potential reservoir of infection and should therefore be immunized against varicella. Other significant nosocomial respiratory viral pathogens, particularly in children and immunosuppressed adults, include respiratory syncytial virus (spread primarily by contact), measles virus (spread by the airborne route), and adenovirus (spread by either respiratory droplets or direct contact). Transmission occurs through contact with other patients, parents, or health care workers with mucosal or digital herpes simplex lesions. Nosocomial transmission is more common with hepatitis B than with other blood-borne pathogens, probably because of its ability to remain viable on environmental surfaces at room temperature for days. The risk is highest with hepatitis B, especially when the source patient is seropositive for hepatitis B e antigen. The risk of infection in non-immune individuals is at least 30% after percutaneous exposure to blood from a hepatitis B e antigen-positive source if no post-exposure prophylactic measures are taken. All health care workers involved in direct patient care should be vaccinated against hepatitis B infection. Recent studies suggest that post-exposure prophylactic treatment with antiretroviral agents may lower the risk even further. No data indicate whether infected workers who do not perform invasive procedures pose a risk to patients.
Cheap flagyl 250mg free shipping. Antimicrobial Resistance Solutions Initiative | Gonorrhoea antibiotic resistance.
Furthermore antibiotic resistance united states purchase discount flagyl on-line, because levodopa "primes" for the development of dyskinesia cowan 1999 antimicrobial discount 400mg flagyl with visa, the use of dopamine agonists before levodopa seems to antibiotic resistance of helicobacter pylori in u.s. veterans buy flagyl 400mg with visa be a prudent practice. When patients continue to be troubled by their parkinsonian symptoms despite deprenyl, anticholinergics, amantadine, and a dopamine agonist, levodopa combined with carbidopa, a peripheral dopa decarboxylase inhibitor, is added to the antiparkinsonian regimen. The starting dosage of carbidopa/levodopa is 25 mg/100 mg (controlled release) twice daily, to be gradually increased to three times per day. Failure to respond to levodopa should also suggest the possibility of a wrong diagnosis, drug interaction (concomitant use of dopamine receptor blocking agents such as antipsychotic and antiemetic drugs), and pharmacokinetic reasons such as insufficient dosage, slow stomach emptying, and competition for absorption in the small intestine and at the blood-brain barrier by amino acids in protein meals. Although non-neuronal elements may participate in the conversion of levodopa to dopamine, the surviving striatal dopaminergic terminals progressively lose their capacity for conversion of levodopa to dopamine, and motor fluctuations and symptomatic deterioration subsequently develop. The post-synaptic dopamine receptors also seem to play an important role in the pathogenesis of motor fluctuations. Tolcapone has a longer half-life (2 hours versus 1 hour) and can be administered three times per day, whereas entacapone requires more frequent administration. Tolcapone may also cause potentially serious liver abnormalities, so liver function must be monitored every 2 weeks. This traditional procedure is being replaced by pallidotomy and high-frequency deep brain stimulation, with the stimulating electrode stereotactically implanted in one of the three target nuclei: thalamus, subthalamic nucleus, or globus pallidus (internal segment). As with all progressive, disabling diseases, psychological support of patients and families offers important help. Patients should be encouraged to learn about their disease (by reading educational material provided by national and local support organizations) and, above all, to remain physically and socially active. Although the virus or viruses responsible for encephalitis lethargica were never isolated, infections caused by Coxsackie, Japanese B, and western equine encephalitis viruses have since been identified as being complicated by parkinsonism. In general, post-encephalitic parkinsonism has a slower progression and is more sensitive to levodopa therapy. The same drugs can also cause a variety of other movement disorders such as akathisia, dystonic reactions, and various tardive syndromes. Levodopa therapy usually fails, probably because ischemia damages the striatal post-synaptic receptors. Typically, but not always, a central spot of hypointensity surrounded by a circumscribed region of hyperintensity gives the appearance of an "eye of the tiger. The combination of parkinsonism and cerebellar ataxia characterizes olivopontocerebellar degeneration or atrophy, a heterogeneous group of neurodegenerative disorders most often inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern, but occasionally occurring sporadically. Later, upward and then lateral conjugate gaze also become impaired, but until the advanced stage, the external ophthalmoparesis can be overcome by labyrinthine stimulation via the oculocephalic maneuver. Patients with progressive supranuclear palsy often exhibit axial rigidity, nuchal dystonia, and a rigid-dystonic facial expression. A clinicopathologic correlation of a large series of cases of Shy-Drager syndrome, olivopontocerebellar atrophy, and striatonigral degeneration. This study showed that early onset, presence of falls, slowness, and early downward-gaze palsy correlated with rapid progression. Essential tremor typically produces flexion-extension oscillation of the hands at the wrists or adduction-abduction movements of the fingers when the arms are outstretched in front of the body. Although frequently referred to as "benign essential tremor," it may be partially disabling, often causing spilling of liquids and interfering with handwriting. Essential tremor also frequently involves the head and voice, which helps differentiate it from parkinsonian tremor. Another useful distinguishing feature is the occurrence of essential tremor during maintenance of posture; parkinsonian tremor is usually present when the affected body part is at relative rest. The frequency of essential tremor ranges from 4 to 12 Hz, and the oscillation may be produced by either alternating or synchronous contractions of antagonistic muscles. Such focal task-specific tremors may be associated with task-specific dystonias ("occupational cramps") or with generalized essential tremor and dystonia. Nearly half of all patients with essential tremor show evidence of an associated dystonia. Essential tremor is an autosomal dominant disorder with a relatively high penetrance. Genetic heterogeneity in essential tremor is very likely given the different familial patterns characterized by either pure essential tremor or essential tremor in combination with dystonia or parkinsonism. Other occasionally useful drugs include primidone (starting dosage, 25 mg at bedtime; the daily dosage can be gradually increased to 750 mg/day), lorazepam, and alprazolam.

In tropical areas it is advisable to antibiotic shelf life order flagyl without prescription hike on clear paths antibiotic induced colitis order 500mg flagyl amex, to antimicrobial or antimicrobial safe 200 mg flagyl avoid thick grass or brush, and to check the inside of shoes, closets, and drawers before extending feet or hands into them. Automobile and other accidents are important causes of morbidity and mortality among travelers. They should inquire about potential risks to their safety before exploring new areas or swimming, particularly in the ocean, where tides may be dangerous. Travelers should seek expert medical evaluation if a high fever develops because it may herald malaria or another life-threatening tropical infection, bloody diarrhea, or other severe symptoms. Lists of reputable physicians can be obtained from American embassies or consulates or from travel insurance companies. Published biweekly, listing countries or areas reporting yellow fever, cholera, and plague. A summary of guidelines for travel and routine immunization with detailed information about vaccines. Gram-positive organisms retain the dye and contain teichoic acids in their cell walls, whereas gram-negative bacteria have an additional outer membrane containing lipopolysaccharide (endotoxin). Capsules may serve as major virulence factors by interfering with the ability of phagocytes to ingest the encapsulated organisms. The capsules ofthe pneumococcus and Haemophilus influenzae are important factors for the virulence of the organisms. Other virulence factors include exotoxins released from the microbe, such as tetanus toxin and cholera toxin. Many gram-negative bacteria contain potent endotoxins that are important mediators of the sepsis syndrome. Pili or fimbriae are small hairlike structures that mediate bacterial attachment to various tissues and body surfaces. Bacteria may be separated by their ability to reside and replicate intracellularly. The main technique used for identification of bacteria in patient specimens is culture on artificial media. Anaerobes cannot grow under such conditions, and facultative organisms can grow either aerobically or anaerobically. Figure 317-1 (Figure Not Available) Cross-section through a generalized bacterial cell. Clin Infect Dis 25:1-10, 1997; Jousimies-Somer H, Summanen P: Microbiology terminology update: Clinically significant anaerobic gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria [excluding spirochetes]. These agents occasionally cause major adverse reactions, interact with other classes of pharmacologic agents, and exert a major selective pressure for widespread antimicrobial resistance among bacteria. For example, the peptidoglycan rigid cell wall is unique to bacteria and thus a target for selective activity by beta-lactam antibiotics. In contrast to humans who can use exogenous folic acid, bacteria cannot use exogenous tetrahydrofolic acid (folinic acid) in the synthesis of nucleic acids and must synthesize folinic acid from p-aminobenzoic acid. Inhibition of this pathway by sulfonamides or trimethoprim, independently or together, thus results in selective antibacterial activity. Antimicrobial agents that inhibit the growth of microorganisms are bacteriostatic, whereas those that kill bacteria at physiologically achievable concentrations are bactericidal. For example, chloramphenicol, which is generally bacteriostatic even at high concentrations, is bactericidal for Haemophilus influenzae at concentrations achieved in patients with standard doses. The site of action and antibacterial effect of major classes of antimicrobial agents are shown in Table 318-1. The sequential inhibition of tetrahydrofolic acid by a sulfonamide and trimethoprim may cause synergism. The mechanism used by individual bacteria to resist specific antimicrobials can be viewed as a strategy to subvert these requirements for antimicrobial efficacy (Table 318-2). Resistance to an antimicrobial agent may be an intrinsic property of a bacterial species or an acquired capability. Exclusion of effective amounts of an antibiotic from intracellular compartments is a common mechanism of intrinsic resistance. The permeability of this membrane resides in special proteins, porins, which provide specific channels through which substances can pass to the periplasmic space and thereafter into the cell. Limited permeability accounts for the intrinsic resistance of gram-negative bacilli to penicillin, erythromycin, clindamycin, and vancomycin; Pseudomonas aeruginosa to trimethoprim; and streptococci as well as enterococci to aminoglycosides. In general, however, mutations to decrease porin channels and reduce permeability are inefficient mechanisms for bacterial resistance and require a second mechanism.