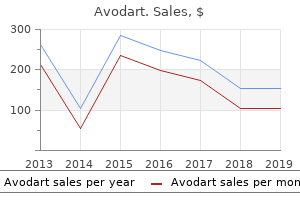
"0.5 mg avodart, medicine zocor".
By: L. Ford, M.B.A., M.B.B.S., M.H.S.
Professor, University of Colorado School of Medicine
The use of cycloplegic in elderly persons with shallow anterior chamber is contraindicated because it can precipitate an attack of acute congestive glaucoma symptoms 0f a mini stroke purchase cheapest avodart. An objective measurement of the state of refraction of the eye when focused for near vision is known as dynamic retinoscopy medicine youth lyrics purchase avodart 0.5 mg line. Since some amount of astigmatism may occur due to medicine reaction order avodart on line amex lenticular factors, the technique is not reliable in determining the total astigmatic error of a patient except in aphakia. Keratometry is based on the fact that the front surface of the cornea acts as a convex mirror and the size of the image of an object reflected by it varies inversely with its curvature. The mires are reflected on the cornea of the patient and one observes four images of the mires through the telescope. The radius of curvature and refractive power can be read from a graduated scale attached to the arc. In the presence of astigmatism, the mires will overlap or separate, hence, readjustment is required. Generally, the mire is so constructed that each step corresponds to 1 D of astigmatism. The mires appear grossly distorted in irregular astigmatism and no useful reading can be obtained. Baush and Lomb keratometer measures both refractive power (in diopters) and radius of curvature (in mm) of the cornea. In addition to an original image there are 2 adjustable images, one above and one to the left. The adjustable images are moved towards or away from the original by changing the distance between the eyepiece and the prism. The post-mydriatic test should be delayed for 2 weeks when atropine is used, for 48-72 hours if homatropine or cyclopentolate is applied and for a day following tropicamide-induced cycloplegia so that the physiological ciliary tone is restored. An exception is made in cases of infants and young children for whom glasses are prescribed after making allowances for cycloplegia and working distance from the retinoscopic findings. As a general rule, the weakest concave lens or the strongest convex lens (in myopia and hypermetropia, respectively) from the trial case. The same procedure is repeated for the occluded eye and finally the acceptance is verified binocularly. In this method, the patient is made myopic by 1 D by addition or subtraction from the retinoscopic findings. If the vision does not improve to 6/6, cylindrical lenses should be tried as per the retinoscopy. The axis of cylinder should be rotated a few degrees Determination of the Refraction 39. The degree and axis of astigmatism can be determined by the use of either an astigmatic fan. But if there is astigmatism, he sees some of the lines more clearly than the others. In the presence of astigmatism, the patient will see some of the lines more sharply defined. Concave cylinder is now added with its axis at right angles to the clearest line until all the lines appear equally clear. A cross-cylinder is a combination of two equal cylinders of opposite signs with their axes at right angles. It is used for subjective refinement of the axis and the power of the prescribed cylinder. Jackson cross-cylinder enlarges or contracts the interval of Sturm, blurring or clarifying the image formed on the retina, by increasing or decreasing the astigmatic ametropia. To check the strength of the cylinder in the optical correction, the axis of the cross-cylinder is first placed in the same direction as to the axis of the cylinder in the trial frame and then perpendicular to it. If in both the instances visual acuity remains unchanged, the cylinder in the trial frame is correct. Should the visual acuity change, a suitable alteration in the strength of the cylinder is to be made.
School-age children with vision impairment can also experience lower levels of educational achievement (71 treatment bursitis order 0.5 mg avodart with amex, 72) and self-esteem than their normally-sighted peers (73) medicine order online avodart. Studies have consistently established that vision impairment severely impacts quality of life (QoL) among adult populations (10 medicine reactions purchase avodart visa, 65, 74-76) and a large proportion of the population rank blindness as among their most feared ailment, often more so than conditions such as cancer (77, 78). Adults with vision impairment often have lower rates of workforce participation and productivity (79, 80) and higher rates of depression and anxiety (16-18) than the general population. In the case of older adults, vision impairment can contribute to social isolation (81-83), difficulty walking (84), a higher risk of falls and fractures, particularly hip fractures (85-91) and a greater likelihood of early entry into nursing or care homes (92-94). It may also compound other challenges such as limited mobility or cognitive decline (95, 96). Vision impairment has serious consequences across the lifecourse, many of which can be mitigated by timely access to quality eye care and rehabilitation. In general terms, people with severe vision impairment experience higher rates of violence and abuse, including bullying and sexual violence (97-100); are more likely to be involved in a motor vehicle accident (101, 102); and can find it more difficult to manage other health conditions, for example being unable to read labels on medication (13-15). While the number of people with severe vision impairments is substantial, the overwhelming majority have vision impairments that are mild or moderate (61). Yet very little is known about the consequences of mild and moderate vision impairment on, for example, infant and child development, educational achievement, workforce participation, and productivity. Impact on family members and carers Support from family members, friends, and other carers is often crucial but can have an adverse impact on the carer. Family members, friends and other carers are often responsible for providing physical, emotional and social support for those with severe vision impairment (104). Examples of such support include accompanying children to school; assistance with activities of daily living. Evidence suggests that support from family members has a positive influence on those with vision impairment and can lead to improved adaptation to vision impairment, greater life satisfaction (106, 107), fewer depressive symptoms (106) and improved uptake of rehabilitative services and assistive products (108). However, providing such support may have detrimental consequences on the caregiver 15 and lead to an increased risk of physical and mental health conditions (109), such as anxiety (110) and depression (111). This is more likely to occur when the caregiver has difficulty balancing their own needs with those of the family member, or when money is short (104). Over and above the support of family, friends and other care givers, a societal response is essential. Impact on society Vision impairment poses an enormous global financial burden due to productivity loss. In addition, the societal burden of vision impairment and blindness is substantial given its impact on employment, QoL and the related caretaking requirements. Vision impairment also poses an enormous global financial burden as demonstrated by previous research that has estimated costs of productivity loss (79, 80, 113, 114). Of particular note, the economic burden of uncorrected myopia in the regions of East Asia, South Asia and South-East Asia were reported to be more than twice that of other regions and equivalent to more than 1% of gross domestic product (80). Participation in daily activities and social roles of older adults with visual impairment. Communication and psychosocial consequences of sensory loss in older adults: overview and rehabilitation directions. Visual impairment is associated with physical and mental comorbidities in older adults: a cross-sectional study. Double jeopardy: the effects of comorbid conditions among older people with vision loss. Help needed in medication self-management for people with visual impairment: case-control study. The incidence and predictors of depressive and anxiety symptoms in older adults with vision impairment: a longitudinal prospective cohort study. Patterns of ophthalmic emergencies presenting to a referral hospital in Medina City, Saudi Arabia. Saudi Journal of Ophthalmology; official journal of the Saudi Ophthalmological Society. Promoting healthy vision in students: progress and challenges in policy, programs, and research. Comprehending the impact of low vision on the lives of children and adolescents: a qualitative approach. Quality of life research: an international journal of quality of life aspects of treatment, care and rehabilitation. Physical activity and social engagement patterns during physical education of youth with visual impairments.
Distance visual acuity is commonly assessed using a vision chart at a fixed distance (commonly 6 metres (or 20 feet) (55) symptoms ulcer stomach purchase avodart 0.5 mg visa. The smallest line read on the chart is written as a fraction symptoms zoloft dose too high buy generic avodart 0.5 mg on line, where the numerator refers to 400 medications discount avodart 0.5 mg with amex the distance at which the chart is viewed, and the denominator is the distance at which a "healthy" eye is able to read that line of the vision chart. For example, a visual acuity of 6/18 means that, at 6 metres from the vision chart, a person can read a letter that someone with normal vision would be able to see at 18 metres. Near visual acuity is measured according to the smallest print size that a person can discern at a given test distance (60). In population surveys, near visual impairment is commonly classified as a near visual acuity less than N6 or m 0. Classification of severity of vision impairment based on visual acuity in the better eye Category Visual acuity in the better eye Worse than: Mild vision impairment Moderate vision impairment Severe vision impairment Blindness Near vision impairment 6/12 6/18 6/60 3/60 N6 or M 0. Severe visual impairment and blindness are also categorized according to the degree of constriction of the central visual field in the better eye to less than 20 degrees or 10 degrees, respectively (62, 63). At that time, the prevalence of vision impairment was calculated based on best-corrected (i. The cut-off for categorizing vision impairment was a best-corrected visual acuity of less than 6/18, while blindness was categorized as a best-corrected visual acuity of less than 3/60. As a result, "best-corrected" visual acuity was replaced with "presenting" visual acuity (i. Measuring "presenting visual acuity" is useful for estimating the number of people who need eye care, including refractive error correction, cataract surgery or rehabilitation. However, it is not appropriate for calculating the total number of people with vision impairment. For this reason, the term "presenting distance vision impairment" is used in this report, but only when describing previous published literature that defines vision impairment based on the measure of "presenting visual acuity". To calculate the total number of people with vision impairment, visual acuity needs to be measured and reported without spectacles or contact lenses. However, a (smaller) body of literature (64) shows that unilateral vision impairment impacts on visual functions, including stereopsis (depth perception) (64). As with bilateral vision impairment, persons with unilateral vision impairment are also more prone to issues related to safety. Further studies report that patients who undergo cataract surgery in both eyes have more improved functioning than patients who undergo surgery in one eye only (66). Nevertheless, effective interventions are available for most eye conditions that lead to vision impairment. These include: a) Refractive errors, the most common cause of vision impairment, can be fully compensated for with the use of spectacles or contact lenses, or corrected by laser surgery. However, effective treatments and surgical interventions are available which can either delay or prevent progression. Given that cataracts worsen over time, people left untreated will experience increasingly severe vision impairment which can lead to blindness and significant limitations in their overall functioning. The examples described above underscore two important issues: first, effective interventions exist for the vast majority of eye conditions that can cause vision impairment; and secondly, access to interventions can significantly reduce, or eliminate, vision impairment or its associated limitations in functioning. A person with an eye condition experiencing vision impairment or blindness and facing environmental barriers, such as not having access to eye care services and assistive products, will likely experience far greater limitations in everyday functioning, and thus higher degrees of disability. Addressing the eye care needs of people with vision impairment or blindness, including rehabilitation, is of utmost importance to ensure optimal everyday functioning. Consequences for individuals Vision impairment has serious consequences across the life-course, many of which can be mitigated by timely access to quality eye care and rehabilitation. Not meeting the needs, or fulfilling the rights, of people with vision impairment, including blindness, has wide-reaching consequences. Existing literature shows that insufficient access to eye care and rehabilitation and other support services can substantially increase the burden of vision impairment and degree of disability at every stage of life (68, 69).
Glioma treatment 247 buy generic avodart 0.5 mg on line, meningioma symptoms 12 dpo buy 0.5 mg avodart overnight delivery, melanocytoma and hemangioma are described in the chapter on Diseases of the Orbit medications requiring aims testing avodart 0.5 mg overnight delivery. The optic nerve is secondarily involved in retinoblastoma, malignant melanoma of the choroid and intracranial meningioma. The localization of lesions of the visual pathway has a great importance in neuro-ophthalmology. The imaginary line dividing nasal and temporal fibers passes through the center of fovea. All temporal fibers lying lateral to the line do not cross, while the nasal fibers cross to the opposite optic tract in the chiasma. Because of this orderly arrangement, the superior visual field is projected onto inferior retina, the nasal field onto temporal retina, the inferior visual field onto superior retina and the temporal field onto nasal retina. Owing to this inverted relationship, lesions of the retina cause defects in the corresponding opposite visual field. Lesions of the Optic Nerve Involvement of both the optic nerves causes complete blindness with the absence of pupillary. If only one optic nerve is damaged, it results in ipsilateral blindness with loss of ipsilateral direct and contralateral consensual pupillary reactions. The lesion of the proximal part of optic nerve results in ipsilateral blindness and contralateral superotemporal field defect (Traquair junctional scotoma) due to looping of crossed fibers in the optic nerve of opposite side. Lesions of the Optic Chiasma the nasal fibers, which constitute about 60% of the total fibers, cross in the chiasma to the opposite optic tract. The fibers from the lower and nasal quadrants of the retina bend medially into the anterior portion of chiasma. After crossing, the anterior fibers in the chiasma loop into the optic nerve of opposite side. The chiasmal fibers, because of their closeness to pituitary gland, are liable to be compressed by enlargement of the gland resulting in optic atrophy. As one side is usually compressed before the other, the earliest defect is a unilateral scotoma. An intra-sellar or extra-sellar tumor produces pressure upon the chiasma and causes early loss in the upper half of field, while supra-sellar tumors cause early loss in the lower half of visual field, and later bitemporal hemianopia may develop. When there is loss of the temporal half of one field of binocular vision and the nasal half of the other field the condition is called as homonymous hemianopia. Lesions of the Visual Pathway 327 pretectal area in the midbrain where they synapse. The association of hemianopia with contralateral third cranial nerve palsy and ipsilateral hemiplegia indicates an optic tract lesion. Syphilitic and tuberculous meningitis, tumors of optic thalamus, tentorial meningioma and aneurysm of the superior cerebellar and posterior cerebral arteries cause optic tract lesions. Lesions of the Optic Tract the optic tract carries uncrossed temporal fibers of the same side and crossed nasal fibers of the opposite side, therefore, a lesion of the tract results in homonymous hemianopia. As the arrangement of the nerve fibers in the tract is not regular, lesions of the tract give incongruous (two sides not exactly equal) homonymous hemianopia. The afferent pupillary fibers (20%) accompany the visual fibers in the optic tract and reach the Lesions of the Optic Radiations the visual fibers running between the lateral geniculate bodies and the occipital lobe constitute the optic radiations. The fibers from the temporal upper quadrant of the ipsilateral and the nasal upper quadrant of the contralateral retina are present in the upper half of the radiation, while the lower half of the radiation represents the lower quadrants of the corresponding retina. As the nerve fibers in the optic radiations are regularly arranged, the lesions of the optic radiations (brain abscess, tumors and vascular lesions) give congruous homonymous hemianopia. More superiorly, the visual fibers travel posteriorly through the parietal lobe of brain. The lesion of the temporal lobe causes complete superior homonymous quadrantanopia. The macular fibers are spared owing to their widespread but segregated course in the optic radiations and their dual representation. Lesions of the Visual Cortex the visual cortex is an area above and below the calcarine fissure which extends into the floor of the fissure as well as to the posterior pole of the occipital cortex. The lesions of the visual cortex classically produce homonymous hemianopic field defects.
Discount avodart 0.5 mg without a prescription. [MR REMOVED] SHINee - Hitchhiking.