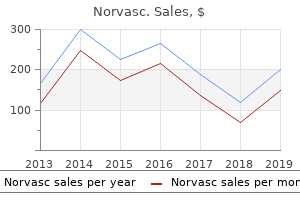
"Cheap norvasc 5mg fast delivery, quitting high blood pressure medication".
By: Q. Milten, M.A., M.D.
Deputy Director, Meharry Medical College School of Medicine
Corticosteroid-Induced Myopathy Myopathies are a group of muscle diseases whose common principal symptom is weakness blood pressure chart bpm order generic norvasc on-line, usually in the proximal muscles of the shoulder and hip joints heart attack 50 years order norvasc 2.5 mg otc. Steroid myopathies most commonly occur in patients who undergo high-dose blood pressure 160 100 buy genuine norvasc, long-term corticosteroid therapy. These patients generally show recovery after decreasing or discontinuing medication. Myopathy patients usually present with difficulty climbing stairs, rising from chairs, and performing transfers. As patient strength improves, gait training under the supervision of a physiatrist and physical therapist can continue on an outpatient basis. Avascular Necrosis and Osteoporosis Avascular necrosis and osteoporosis frequently occur in cancer patients. These problems are diagnosed radiographically and may be asymptomatic until the involved bone is subject to fracture or infection. Glucocorticosteroids inhibit new bone formation and calcium absorption and increase bone resorption and renal calcium excretion. More than 50% of patients taking long-term steroids develop some degree of osteoporosis (Goroll et al. The risk of developing steroid-induced osteoporosis can be reduced by using a short-acting preparation at the lowest possible dose in an alternate-day regimen, by maintaining physical activity, and by ensuring adequate daily intake of calcium and vitamin D. Therapies used to slow down bone involution and prevent contracture formation and postural deviations: weight-bearing exercises, upper and lower extremity muscle strengthening, balance training, back extension and chest expansion exercises, pectoralis muscle stretching, posture correction, and proper lifting techniques 2. Hormone replacement therapy for men and women who do not have contraindications 4. Environmental modification: proper footwear, adjustment of medications that may contribute to falling; assistive devices 8. Education of patients regarding risk factors such as smoking Compression fractures may ensue with only minor trauma once sufficient structural integrity is lost. Pain may be managed with analgesic and anti-inflammatory medications and the use of spinal orthoses. Early weight-bearing and limited immobilization should be encouraged to minimize continued bone loss. Contracture of Joints A limitation of passive joint range of motion, contracture commonly results from a restriction in connective tissue, tendons, ligaments, muscles, and joint elements. Contractures are most often related to spasticity, bed rest, localized heterotopic ossification, bleeding, infection, trauma, and edema. Prevention is achieved by minimizing the duration of bed rest and encouraging daily range of motion exercises. Heterotopic Ossification Heterotopic ossification is the formation of mature, lamellar bone in soft tissues. The variable incidence of heterotopic ossification has been reported in spinal cord injury patients (20% to 25%) and in head injury patients (10% to 20%) (An et al. The chief symptoms of heterotopic ossification are joint and muscle pain and compromised range of motion. A triple-phase bone scan is able to detect heterotopic ossification at an early stage. Shoulder pain may originate from rotator cuff tears, bicipital tendinitis, adhesive capsulitis, and subdeltoid bursitis. Other causes of shoulder pain in the hemiplegic population include excessive shoulder capsule stretch secondary to paresis of shoulder musculature, sympathetically maintained pain (reflexsympathetic-dystrophy, shoulder-hand syndrome), and thalamic syndrome. Immobilization can contribute to intellectual, emotional, and behavioral disturbances, decreased muscle strength and endurance, poor coordination, and contracture of joints. Cardiovascular and pulmonary deconditioning may present with orthostatic hypotension, deep vein thrombosis, decreased vital capacity, and impairment of the cough mechanism. Anorexia, constipation, electrolyte disturbances, and pressure ulcers are also manifestations of immobilization (Hoffman et al. Physical therapy should begin early, emphasizing progressive mobilization, starting with passive range of motion if necessary; progressing to assisted active range of motion; then to active range of motion. When postural hypotension is pronounced or when patients have been or are expected to be bed bound for more than one week, tilt-table use should begin as soon as the patient is stable. This device is beneficial for cardiovascular and respiratory reconditioning and can also help prevent osteoporosis. Once the patient tolerates a 70-degree angle for 30 minutes, standing and ambulation should begin.
Treatment is required for symptomatic relief of raised intracranial pressure and to blood pressure ranges by age and gender order norvasc 5 mg with visa minimise the risk ofneurologicaldamage blood pressure chart 16 year old purchase discount norvasc online. Clinical features In infants with hydrocephalus blood pressure levels chart cheap 2.5mg norvasc fast delivery, as their skull sutures havenotfused,theheadcircumferencemaybedispro portionatelylargeorshowanexcessiverateofgrowth. The skull sutures separate, the anterior fontanelle bulges and the scalp veins become distended. Hydrocephalus may be diagnosed on antenatal ultrasoundscreeningorinpreterminfantsonroutine cranialultrasoundscanning. Forsuspectedhydroceph alus, initial assessment is with cranial ultrasound (in the neurocutaneous syndromes Thenervoussystemandtheskinhaveacommonecto dermal origin. Thecutaneousfeaturesconsistof: Thecutaneousfeaturestendtobecomemoreevident afterpuberty,andthereisawidespectrumofinvolve ment from mild to severe. Neurofibromata appear in the course of any peripheral nerve, including cranial nerves. Theymaylookunsightlyorcauseneurological signs if they occur at a site where a peripheral nerve passes through a bony foramen. Other associations are phaeochromocytoma, pul monaryhypertension,renalarterystenosiswithhyper tension,andgliomatouschange,particularlyincentral nervous system lesions. These children have severe learning difficulties and often have autistic features to their behaviour when older. Children presenting with intractable epilepsy in earlyinfancymaybenefitfromhemispherectomy. For children who are less severely affected, deterioration is unusual after the age of 5 years, although there maystillbeseizuresandlearningdifficulties. The ophthalmic division of the trigeminal Neurodegenerative disorders Thesearedisordersthatcauseadeteriorationinmotor and intellectual function. Lysosomal storage disorders In metachromatic leucodystrophy, a sulfatidosis, an accumulation of sulphatides causes a destruction of myelinandisdiagnosedontestingwhitecellenzymes. Other Hepatosplenomegaly Conductive deafness Umbilical and inguinal hernias Table 27. The mucopolysaccharidoses are progressive multi system disorders which may affect the neurological, ocular,cardiacandskeletalsystems(Table27. It is onlyinthesecond6monthsoflifethatthecharacter istic facies begin to emerge, with coarsening of the facialfeaturesandprominentforeheadduetofrontal bossing(Fig. Successful enzyme replacement by bone marrow transplantation has been performed but cannot reverse any established neurological abnormality. Summary In neurodegenerative disorders There is developmental regression with the evolu tionofabnormalneurologicalsigns. Websites (Accessed May 2011) British Paediatric Neurology Association: Available at. International Headache Society classification: Available at: /ihs-classification.
Cheap norvasc master card. Alcohol Withdrawal Home Remedies by Sachin Goyal @ ekunji.com.
The cavity usually result from the pre-existing tuberculosis blood pressure log template purchase norvasc 5mg mastercard, bronchiactasis heart attack water discount norvasc line, old infracts and abscesses hypertension high blood pressure purchase norvasc 5 mg overnight delivery, Invasive Aspargilosis It is an opportunistic infection confined to immunosupressed and debilitated hosts. The Aspargilus Species have a tendency to invade blood vessels and thus, areas of hemorrhages and infarction are usually superimposed on necrotizing inflammatory reactions 4. Histoplasmosis and Coccidiomycosis resemble pulmonary tuberculosis and both are causedby fungi that are thermally dimorphic (hyphae and yeast forms) 185 - Natural history of histoplasmosis include. Subsequently secreted interferon gamma activates macrophages to kill intracellular yeasts. Morphology: Granulomatous inflammation with areas of solidifications that may liquefy subsequently. Fulminant disseminated histoplasmosis is seen in immunocompromized individuals where immune granulomas are not formed and mononuclear phagocytes are stuffed with numerous fungi throughout the body. Viral tropism -in part caused by the binding of specific viral surface proteins to particular host cell surface receptor proteins. The second major cause of viral tropism is the ability of the virus to replicate inside some cells but not in others. Once attached the entire viron or a portion containing the genome and the essential polymerase penetrate into the cell cytoplasm in one of the three ways 1) 2) Translocation of the entire virus across the plasma membrane Fusion of viral envelop with the cell membrane or 186 3) Receptor -mediated endocytosis of the virus and fusion with endosomal membranes Within the cell, the virus uncoats separating its genome from its structural component and losing its infectivity. Newly synthesized viral genome and capsid proteins are then assembled into progeny virons in the nucleus or cytoplasm and are released directly (unencapsulated viruses) or bud through the plasma membrane (encapsulated viruses) Viral infection can be abortive with incomplete replicative cycle Latent in which the virus (eg herpes zoster) persists in a cryptic state within the dorsal root ganglia and then present with painful shingles Or persistent in which virons are synthesized continuously with or without altered cell function (eg. Viruses replicate effiently and lyse host cell ex yellow fever virus in liver and neurons by poliovirus. Viral proteins on the surface of the host cell are recognized by the immune system, and the host cytotoxic lymphocytes then attack the virus-infected cells ex hepatitis B virus infection, and respiratory synaytial virus. Viral killing of one cell type causes the death of other cells that depend on them, Example poliovirus cause motor neuron injury and atrophy of distal skeletal muscle. Slow virus infection cause in severe progressive disease after a long latency period for example sub acute pan encephalitis caused by measles virus. Exercise Describe the etiology, pathogenesis, morphologic changes and clinical effects of each of the above mentioned diseases. Definition amd Nomenclature Literally, neoplasia means new growth and technically, it is defined as abnormal mass of tissues the growth of which exceeds and persists in the same excessive manner after cessation of the stimulus, evoking the transformation. Nomenclature: Neoplasms are named based upon two factors on the histologic types: mesenchymal and epithelial on behavioral patterns: benign and malignant neoplasms Thus, the suffix -oma denotes a benign neoplasm. Benign mesenchymal neoplasms originating from muscle, bone, fat, blood vessel nerve, fibrous tissue and cartilages are named as Rhabdomyoma, osteoma, lipoma, hemangioma, neuroma, fibroma and chondroma respectively. Benign epithelial neoplasms are classified on the basis of cell of origin for example adenoma is the term for benign epithelial neoplasm that form glandular pattern or on basis of microscopic or macroscopic patterns for example visible finger like or warty projection from epithelial surface are referred to as papillomas. Malignant neoplasms arising from mesenchymal tissues are called sarcomas (Greed sar =fleshy). These neoplasms are named as fibrosarcoma, liposarcoma, osteosarcoma, hemangiosarcoma etc. Malignant neoplasms of epithelial cell origin derived from any of the three germ layers are called carcinomas. Ectodermal origin: skin (epidermis squamous cell carcinoma, basal cell carcinoma)Mesodermal origin: renal tubules (renal cell carcinoma). Endodermal origin: linings of the gastrointestinal tract (colonic carcinoma) Carcinomas can be furtherly classified those producing glandular microscopic pictures are called Aden carcinomas and those producing recognizable squamous cells are designated as squamous cell carcinoma etc furthermore, when possible the carcinoma can be specified by naming the origin of the tumour such as renal cell adenocarcinoma etc Tumors that arise from more than tissue components: Teratomas contain representative of parenchyma cells of more than one germ layer, usually all three layers. They arise from totipotential cells and so are principally encountered in ovary and testis. Characteristics of Benign and Malignant Neoplasms the difference in characteristics of these neoplasms can be conveniently discussed under the following headings: 1. Differentiation and anaplasia Differentiation refers to the extent to which parenchymal cells resemble comparable normal cells both morphologically and functionally. Thus, well-differentiated tumours 191 cells resemble mature normal cells of tissue of origin.
The study of bias or errors in clinical judgment prehypertension at 36 weeks pregnant cheap norvasc master card, of environmental stimuli blood pressure treatment generic norvasc 5 mg without a prescription, and social desirability complement this approach (Rogler 1996; Weiss 1997) pulse pressure ratio buy discount norvasc on-line. The field of outcomes research offers further support to a culturally strong psychiatric diagnostic system. These areas of investigation would also encompass family and other support systems, the impact of acculturation, and a more cogent and objective study of the intriguing culture-bound syndromes and idioms of distress. The many cultural nuances of the psychotherapeutic process and the variants related to the cultural makeup of special populations add strength to this objective. Racism and stigmatization are topics that transcend the customary grounds of epidemiologic or outcomes research. The study of these conditions at the individual, structural, and institutional levels will increase the credibility of the diagnostic and nosologic effort. The same applies to the vast implications of gender and psychopathology; to social and cultural realities such as violence and trauma; and to sensitive yet culturally prominent variables such as sexual orientation, religion, and spirituality. In this area, for instance, Gartner (1993) advocates the exploration of mechanisms mediating macrosocial factors and punctual, individual outcomes. Similarly, cultural research on the large topic of disparities in mental health care and its many components (availability, accessibility, quality, and accountability) from patient to care agency and vice versa will have a significant effect on diagnosis. This process of cultural critique not only of psychiatry but also of the research process has been considered a conceptual antidote for such disparities. The diagnostic assessment would not be complete, however, without an estimate of the broad common ground between culture and neurobiology. The old nature versus nurture debate, translated contemporaneously into the genetic-environmental interaction, requires research aimed not only at a definition of the magnitude of each parcel in the life of the mind, the brain, the chromosome, or the community, but mostly at the points of contact operating in each behavioral act or in the chain of events that result in the actions (behaviors) to be observed, diagnosed, cataloged, and treated. It Beyond the Funhouse Mirrors 265 is necessary to biologize culture by thinking through the ways in which culture is an aspect of the biological organization of human beings. By the same token, it is also necessary to culturalize biology by examining how biological models and metaphors are shaped by cultural values and assumptions. Ethnophysiology and ethnopsychopharmacology each have a role in the diagnostic task as confirming or modifying factors; within the next several decades the biocultural study of behavioral traits, specific emotions, and cognitive processes will add information that may very well change the whole nature and conduct of the diagnostic task in psychiatry. Another critical step in this whole process is the articulation of an efficient translation and dissemination system that would generate the development and testing of practical new strategies in diagnosis, service delivery, and treatment (U. How research on mental health diagnosis is understood by professionals and the public and is implemented by agencies and administrators are areas that should themselves be the subject of investigative efforts. Conclusion A diagnosis-oriented cultural psychopathology research agenda integrates ethnographic, observational, clinical, and epidemiologic approaches, each one providing useful information to crystallize into a comprehensive description of a clinical condition with different levels of impact. On the other hand, a systemic approach surpasses, despite some limitations, the mind-body dichotomy while accepting biological, psychological, social, religious, and spiritual components of the human experience. A crucial aspect of all these approaches consists of not ignoring the internal diversity of most communities in terms of ethnic and religious groups, rural versus urban settings, social class, and others-all sources of considerable variability in the clinical and epidemiologic data. In short, a culturally informed diagnosis uses multiple lenses as the researcher moves between lay and professional systems of meaning to make sense out of behavioral observations. Teaching and training present and future professionals on the need to include cultural factors in the diagnostic process is a logical step in any attempt to develop comprehensive research programs in psychology, psychiatry, and related disciplines. Reasons for the slow development of these fields are not only methodological, curricular, or doctrinary. Lee (1994) asserts that the terms culture and social group appear to be "alien and strange to many researchers in the United States. Pellmar and Eisenberg (2000) recently examined the obstacles to interdisciplinary research and training, including attitudinal and communication barriers, the structures and promotion policies of academic institutions, and obstacles from funding organizations and peer review processes. Obviously, infrastructure needs for these efforts (different from those of a neurobiological nature) must be addressed. In sum, training of underrepresented minorities and the development of capabilities that integrate social and cultural dimensions in mental health and psychiatric diagnosis would be a crowning effort for a research agenda such as the one outlined in these pages. New York, Harper, 1950 Aguilar-Gaxiola S: World mental health 2000 in the Americas: an initiative of the World Health Organization.