"Generic furadantin 100mg on-line, antibiotics for ear infections".
By: S. Givess, M.A., M.D., M.P.H.
Vice Chair, University of Connecticut School of Medicine
Hyperplasia: this is an increase in size of a tissue or organ due to took antibiotics for sinus infection but still sick order furadantin overnight an increased number of individual cells antibiotics for acne in south africa buy generic furadantin 50 mg on-line. It is commonly induced by an increased functional demand (renal interstitial hyperplasia) antibiotics for uti in humans cheap furadantin 50mg without a prescription, physical or chemical irritation (gill epithelium), or excessive hormonal stimulation (thyroid, goiter). Hypertrophy: this is the increase in size of a cell due to synthesis of additional structural components. Hypertrophy is commonly induced by either increased work load, or physical or chemical irritation. Metaplasia: this is a change in which a mature differentiated cell type is replaced by another differentiated type. It comes about due to nutritional abnormalities, constant irritation, or no apparent reason. Dysplasia: this is a disorderly cell growth accompanied by cellular atypia (pleomorphism, hyperchromicity, loss of normal maturation progression). Tumors are incited by a number of mechanisms, from genetic events to toxin exposures to some types of infections. And as control mechanisms are no longer in play, a tumor will persist even if the inciting cause is eliminated. They are allocated to two broad categories, "benign" tumors that are usually (but not always) less deleterious to the host, and "malignant" tumors, those that are more likely (but again not always) to cause the host some degree of harm if not death. Histologic features of tumors are extremely useful in determining whether the lesion is benign or malignant, what its biological activity. Benign tumors tend to be less serious, although there are some benign tumors which can cause the death of the patient. Malignant tumors tend to be more serious in terms of biological consequence to the host. Many malignant tumors will eventually cause the death of the patient by various means, although some can be less aggressive and may not have a serious impact on long term survival. These histological characteristics of benign and malignant tumors are variable for any given tumor, i. When examining a tumor in a histologic preparation, keep track of all observed features and when finished, make your diagnosis based upon this overall picture. Be aware that the distinction between benign and malignant is not always clear cut (except in the presence of metastasis, which by definition means malignant), and that for a given tumor, there may be disagreement between pathologists as to its nature and likely biological activity. Diagnosis of a particular tumor may be very straightforward, particularly if it is a well differentiated neoplasm. But many are not differentiated, and it can be extremely difficult to determine the cell of origin. Special stains can be useful in some cases; for example, poorly differentiated mast cell tumors can sometimes be recognized by the presence of even a few granules that stain with toluidine blue. Immunohistochemistry is an extremely useful technique for the identification of neoplasms. This technology relies upon antibody-based stains specific for intermediate filaments or surface markers. Thus, these can be used as markers to provide evidence that a tumor is of epithelial or connective tissue origin. It will show up to varying degrees in histological preparations, depending upon how quickly sample collection and fixation occurred after death. Autolyzed tissues are obviously not the best samples to use for histological assessments, and care should be taken to minimize their inclusion in your samples. It is important to be able to separate tissue changes due to autolysis from those that are lesions. Cell structure is maintained, and nuclei are faded or absent, similar to karyolysis during necrosis.
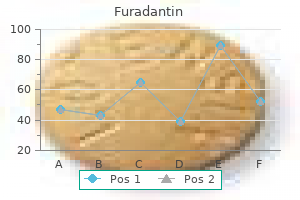
There were 266 male and 208 female adolescents and 475 male and 493 female adults antibiotics for mild acne discount 100mg furadantin fast delivery. Multiple linear regression and logistic regression models were used to antibiotics for uti at walmart buy cheap furadantin on line analyze the data antibiotics for acne trimethoprim cheap furadantin amex. Covariates included age, gender, race, smoking status, alcohol intake, and household income. Fasting insulin and fasting glucose were used to determine the homeostatic model assessment for insulin resistance. Male reproductive endpoints evaluated in humans include sperm count and semen quality (Buck Louis et al. As noted previously, the focus of this review is on pregnancy-related outcomes, specifically pregnancyrelated hypertension and preeclampsia, measures of fetal growth, and pubertal development. Within each section, the discussion is divided into occupational exposure studies (if applicable), the C8 high-exposure community studies, and general population studies. The females (n = 1,400) and their infants were randomly selected, and the study included those who provided their first blood samples between gestational weeks 4 and 14 and gave birth to a single live-born child without congenital malformation. The females participated in telephone interviews-at 12 and 30 weeks gestation, when the children were 6 and 18 months of age, and when the children were 7 years of age-and filled out a food frequency questionnaire. As the children aged, more questionnaires were completed by the mothers with regard to behavioral health and motor coordination. The National Hospital Discharge Register was used to obtain birth weight, gestational age, placental weight, birth length, head and abdominal circumference data, Apgar scores based on heart rate, respiratory effort, reflex, irritability, muscle tone, and skin color. Results of these studies are included in the following discussion of results for specific endpoints. The only data available come from the high-exposure C8 Health Project study population (Table 3-9). Several studies, using different designs and exposure measures, have examined birth outcomes, including pregnancy-induced hypertension or preeclampsia in infants born to mothers in the high-exposure C8 community population in West Virginia and Ohio (information obtained from questionnaire-based pregnancy histories or from linkage to birth records) (Table 3-9). Singleton live births among 1,330 females after January 1, 2005, were linked to birth records to identify outcomes of pregnancy-induced hypertension and other outcomes. Some studies conducted by the panel found no associations while others showed positive associations. Among the studies with positive associations, no clear dose response was indicated. Birth weight is widely available (as it is routinely collected in medical records and birth certificates). Low birth weight (defined as < 2,500 g) can be a proxy measure for preterm birth (particularly when accurate gestational age dating is not available). Other measures of fetal growth such as small for gestation age might more accurately reflect fetal growth retardation. Both birth weight and gestational age are characterized as two-part distributions, with a larger Gaussian portion representing term births and a longer tail representing preterm births. Increased risks of complications, including infant mortality, are seen in preterm births (or low birth-weight births). When analyzed as a continuous measure, changes in birth weight might not be clinically significant, as small changes in the distribution among term infants do not result in a shift into the distribution seen in preterm infants (Savitz 2007; Wilcox 2010). This consideration differs from that of some other types of continuous measures, such as neurodevelopment scales, blood pressure, or cholesterol, in which shifts in the distribution are expected to move a greater proportion of the population into an "at risk" or "abnormal" level. As noted in the previous discussion of preeclampsia, several studies using different designs and exposure measures have examined birth outcomes in infants born to mothers in the high-exposure C8 community population in West Virginia and Ohio (Darrow et al. These studies vary in size from approximately 250 to 1,400 births, and also in terms of timing of exposure measure. These studies also differed in the percent of births that were preterm (ranging from approximately 3% to 13%), and presented results using different types of analyses. In a systematic review based on the Navigation Guide methods (Woodruff and Sutton 2014), Johnson et al. The increases were greater and statistically significant in females with preeclampsia. They identified 35 relevant studies published between 1954 and 2012 that met the Navigation Guide criteria for inclusion in the analysis. When adjusted for confounders, no statistically significant differences were found.
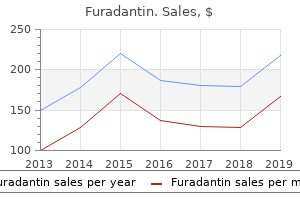
Therefore virus mask purchase cheap furadantin on line, any random variation that may exist is not expected to infection lymph node buy furadantin online pills negatively impact the public health benefit of the proposed standard bacteria at 0 degrees cheap 50 mg furadantin mastercard, which is based on reduction of excess lifetime cancer risk. Information that is incorporated by reference would have the same force and effect as language explicitly stated in the codified. In certain circumstances, it may not be necessary to conduct initial real-time stability testing on a particular product because the results from initial real-time stability testing conducted on another similar product apply. The results from that testing would apply to both products and the testing would be considered to cover both products. Other examples of differences between products that would not require additional initial real-time stability testing, if initial real time stability testing has already been conducted on one of the products, include slight changes in acids, bases, or other pH modifiers with no resulting change in final pH. This provision is intended to reduce the burden on the manufacturer, while ensuring that there is initial realtime stability data that applies to all finished tobacco products, thus preserving the goal of the requirement. Manufacturers would be required to use the results from initial stability testing to establish an expiration date and appropriate storage conditions (either room temperature or refrigeration) for the finished product. We believe that room temperature or refrigeration are the most likely storage conditions for smokeless tobacco products because most current smokeless tobacco products are stored at room temperature while some snus products are refrigerated. The manufacturer would be allowed to use an expiration date of no longer than 1 year based on initial accelerated stability testing. We would require the first time point be within 7 days of manufacture and the last time point at 6 months after manufacture. In addition, finished product that does not conform to the standard would not be released for commercial distribution. We expect that any changes in a rate of increase would be observed and investigated during annual stability testing. This report would need to include the full identification of the smokeless tobacco product that is the subject of the report, including the product subcategory, brand, subbrand, package size and quantity of product (mass and, if portioned, count) and, for portioned tobacco products, the size (mass) of each portion. Subcategories of smokeless tobacco products include, for example, loose moist snuff, portioned moist snuff, loose snus, portioned snus, loose dry snuff, certain dissolvables, loose chewing tobacco, and portioned chewing tobacco. Accordingly, this accelerated data may not be used to forecast an expiration date. Accelerated stability testing would not be permitted for annual stability testing. We propose that accelerated stability testing be permitted for initial stability testing to reduce the time required to bring new products to market without adversely impacting public health. However, accelerated testing is unnecessary for annual stability testing because these products would already be on the market. The manufacturer would be required to keep the records of the decision made and the justification.
Discount 50 mg furadantin with mastercard. Antibiotic Resistance: A Public Health Crisis | Victoria J. Fraser MD | TEDxStLouisWomen.
Syndromes
- Cold or respiratory illness that has been getting better and then begins to get worse
- You develop thoughts that are not based in reality, or you start hearing or seeing things that other people cannot
- Reduced life span for severe forms of the condition
- Neurofibromatosis
- Convulsions
- Kidney failure
- Ovarian cancer
- Cytomegalovirus
- Bufferin
The kidneys are slightly protected by the ribs and are surrounded by fat for protection (not shown) antibiotics for dogs chest infection generic furadantin 100 mg with visa. Internal Anatomy A frontal section through the kidney reveals an outer region called the renal cortex and an inner region called the medulla (Figure) can you get antibiotics for acne purchase 100 mg furadantin amex. The renal columns are connective tissue extensions that radiate downward from the cortex through the medulla to best antibiotics for acne reviews safe furadantin 100mg separate the most characteristic features of the medulla, the renal pyramids and renal papillae. The papillae are bundles of collecting ducts that transport urine made by nephrons to the calyces of the kidney for excretion. Emerging from the hilum is the renal pelvis, which is formed from the major and minor calyxes in the kidney. The smooth muscle in the renal pelvis funnels urine via peristalsis into the ureter. The renal arteries form directly from the descending aorta, whereas the renal veins return cleansed blood directly to the inferior vena cava. The artery, vein, and renal pelvis are arranged in an anterior-to-posterior order. Nephrons and Vessels Blood Flow in the Kidney 99 Nephrons are the "functional units" of the kidney; they cleanse the blood and balance the constituents of the circulation. After passing through the renal corpuscle, the capillaries form a second arteriole, the efferent arteriole (Figure). These will next form a capillary network around the more distal portions of the nephron tubule, the peritubular capillaries and vasa recta, before returning to the venous system. As the glomerular filtrate progresses through the nephron, these capillary networks recover most of the solutes and water, and return them to the circulation. Blood Flow in the Nephron 100 the two capillary beds are clearly shown in this figure. The efferent arteriole is the connecting vessel between the glomerulus and the peritubular capillaries and vasa recta. Visit this link to view an interactive tutorial of the flow of blood through the kidney. About 15 percent of nephrons have long loops of Henle that extend deep into the medulla and are called juxtamedullary nephrons. But the female reproductive system has the additional task of supporting the developing fetus and delivering it to the outside world. Unlike its male counterpart, the female reproductive system is located primarily inside the pelvic cavity (Figure). Identify female reproductive structures, Describe the primary functions of the female reproductive systems Apply word building skills by constructing medical terms related to reproductive systems. Describe common abbreviations used to describe reproductive structures, functions, and medical procedures. Recognize, define, pronounce and spell medical terminology related to the reproductive system correctly 105 Anatomy of the Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive System 106 the major organs of the female reproductive system are located inside the pelvic cavity. External Female Genitals 107 the external female reproductive structures are referred to collectively as the vulva (Figure). The mons pubis is a pad of fat that is located at the anterior, over the pubic bone. The labia majora (labia = "lips"; majora = "larger") are folds of hair-covered skin that begin just posterior to the mons pubis. The thinner and more pigmented labia minora (labia = "lips"; minora = "smaller") extend medial to the labia majora. Although they naturally vary in shape and size from woman to woman, the labia minora serve to protect the female urethra and the entrance to the female reproductive tract.